User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
LuaAutomation ATC rail
 Do anything you want with these ATC rails.
Do anything you want with these ATC rails.
 This is a draft. Please improve this page by creating relevant pages, adding information and references to internal or external sources.
This is a draft. Please improve this page by creating relevant pages, adding information and references to internal or external sources.
Note: this page has been written for Advtrains 2.1.0 and Minetest 5.1.0. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases.
Properties
Mod: advtrains_luaautomation
Node name: advtrains_luaautomation:dtrack_placer
Other names:
advtrains_luaautomation:dtrack_stadvtrains_luaautomation:dtrack_st_30advtrains_luaautomation:dtrack_st_45advtrains_luaautomation:dtrack_st_60
Craft recipe
This node has no craft recipe.
Extended description
- When the rail is first built, this rail node does nothing. But once right-clicking (or double tapping on Android) the node, a formspec displays, allowing you to write Lua code for the current node.
- Interacting with the ATC rail requires the
atlatcprivilege. - The code in the ATC rail is executed when an event is fired. See Events for a list of events this node supports.
- This node can be rotated by the Trackworker.
- Only straight nodes are supported. You can't put this node on a curve or as a switch.
- This node is an active component.
Environments
Each active component is assigned to an environment. This is where all data are held. Components in different environments can't interfere with each other.
Note: the Environments and Coding guide sections also apply to the LuaAutomation operation panel.
Creating an environment
Main article: /env_create
An environment is created by using /env_create. We pass to this command the name of the environment to create. While this name may contain whitespaces and symbols, it is highly recommended that you use only uppercase, lowercase letters and underscores.
Setting up an environment
Main article: /env_setup
You've created your first LuaATC environment! If you execute /env_setup <your_env_name> in the chat window, you get a formspec like this:
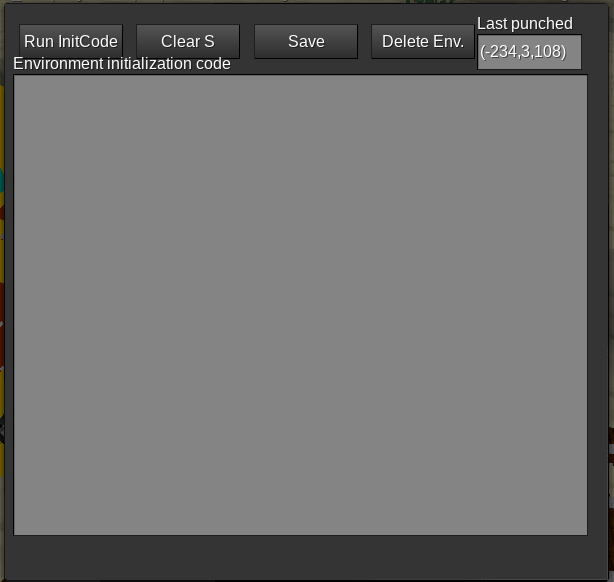
It allows you to edit your environment initialization code.
- The button “Run InitCode” runs immediately the initialization code.
- The button “Clear S” removes all elements from the
Stable. - The button “Save” saves the initialization code for the current environment.
- The button “Delete Env.” is to delete your environment. This may happen when you accidentally created the environment or you no longer need it. You will be asked to confirm by typing YES (in uppercase) into a second formspec. Once it is deleted, all data associated to the environment is lost and can't be recovered.
When the init code fails to execute, the F table is restored to previous state.
More information on how to use that initialization code to do amazing things is given below.
Coding guide
Predefined global variables
The following global variables are available inside a LuaAutomation ATC rail:
S
A table shared between all components of an environment. Its contents are persistent over server restarts. Any value is allowed, except functions:
Do not store functions in this table. Calling them from another component may work, but they will be discarded on server shutdown and this may lead to unexpected results.
F
A table shared between all components of an environment. Its contents are discarded on server shutdown or when the init code gets re-run. Any value is allowed, even functions.
This table is not made to store data, but to provide static value and function definitions. This table should be populated by the initialization code.
Available Lua functions
The standard Lua globals are available in the LuaATC environment:
stringmathtableos
The standard Lua functions are available in the LuaATC environment:
asserterroripairspairsnextselecttonumbertostringtypeunpack
LuaAutomation-specific functions
In the following functions, all parameters named pos designate a position. You can use either:
- a default Minetest position vector (like
{x=34, y=2, z=-18}) - the
POS(34,2,-18)shorthand - a string, the name of a passive component.
POS(x, y, z)
A shorthand function to designate a Minetest position vector like {x=?, y=?, z=?}.
Interacting with switches and other passive components
Switches (turnouts), simple signals and mesecon switches are so-called “passive components”. This is because they can be controlled passively by LuaATC (and by other means). From LuaATC, this happens via a “state” string. The states are as follows:
Switch: "st" - turnout is set to the straight branch "cr" - turnout is set to the diverting (curved) branch Signal: (simple signals, wall signals) "red" - the signal is red "green" - the signal is green Mesecon Switch, Andrew's Cross: "off" - switch is off, Andrew's cross does not blink "on" - switch is on, Andrew's cross blinks and bell rings
getstate(pos)
Gets the state of a passive component at position pos. The returned states are component-specific, as described above.
setstate(pos, new_state)
Sets the state of a passive component at position pos to the value new_state. The returned states are component-specific, as described above.
is_passive(pos)
Checks whether there is a passive component at position pos. If pos is a string, checks whether the passive component with the specified name exists.
Interrupts
These functions allow to schedule interrupts, a.k.a events to be executed at a later time. They are not available in init code.
The time counter and queue handling these interrupts is synchronized to minetest's internal step time. It is written in a very simple fashion, and is NOT secured against “interrupt bombs”. Be careful!
-- an example for an "interrupt bomb"
-- NEVER DO THIS!
if event.int then
interrupt(1,"A")
interrupt(1,"B")
-- run 1: {A,B}
-- run 2: {A,B,A,B}
-- run 3: {A,B,A,B,A,B,A,B}...
interrupt(time, message)
Causes the LuaAutomation mod to trigger an int event (the Advtrains equivalent of Mesecons' interrupt) on this component after the given time, in seconds, with the specified message. message can be of any Lua data type.
interrupt_pos(pos, message)
Triggers immediately an ext_int event on the active component at pos (can't be a string). message can be of any Lua data type.
Railway Time
When advtrains_line_automation is enabled, all Railway time functions are exposed as rwt.* and can safely be used in LuaATC code.
For the available functions, see rwt.
--Example: print the time of the next full minute local now = rwt.now() local next_minute = rwt.next_rpt(now, "01;00", 0)
Railway Time Scheduler
This is a separate schedule queue. In contrast to the interrupt system, which is the original and established way to schedule interrupts, it relies on the Railway Time system and therefore is only accessible when advtrains_line_automation is enabled.
There are two important considerations to this:
- While the interrupt system is always synchronized to minetest step time, the RWT scheduler follows the RWT time flow. In particular, this means that you must be able to handle “time jumps” that occur when RWT is set up to adapt to real time.
- The RWT scheduler has a built-in protection against “interrupt bombs”. There is a limit on how many interrupts can be enqueued from a single LuaATC component. At the time of this writing, this limit is set to
1.
Clicking “Save” on the code edit form clears all events currently scheduled in the RWT scheduler. It does NOT clear the interrupt scheduler events.
schedule(rwtime, msg)
Triggers a schedule event AT the specified Railway Time.
The time value here is an absolute value.
msg can be any data type and is accessible in event.msg.
schedule_in(rwtime, msg)
Like schedule(), but the passed time is relative.
-- Example: schedule a "depart" event in 1 minute
schedule_in("01;00", "depart")
Digiline
digiline_send(channel, message)
Sends a digiline message on the specified channel.
This function is not available in init code.
Interlocking functions
Interlocking functions are available when the advtrains_interlocking mod is enabled.
can_set_route(pos, route_name)
Checks whether it is possible to set the route designated by route_name from the signal at position pos.
It emits a warning and halts execution of Lua code in the following cases:
- the node at specified position is not a signal:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …ds/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/environment.lua:168: There's no signal at (0,0,0)
posis a string, and the named passive component does not exist:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …/mods/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/pcnaming.lua:22: Invalid position supplied to ???: “invalid_pcnaming”
- the specified route does not exist:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …ds/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/environment.lua:185: No route called B at (0,0,0)
set_route(pos, route_name)
Requests the route designated by route_name from the signal at position pos. Has the same effect as clicking the “Set Route” in the formspec from the designated signal.
Same warnings apply as for can_set_route.
If the route can't be set, the signal remains red and waits for conflicting problems to be solved. Execution continues immediately.
cancel_route(pos, route_name)
Cancels the route designated by route_name that is set from the signal at position pos. Has the same effect as clicking the “Cancel Route” in the formspec from the designated signal.
Same warnings apply as for can_set_route.
If the route has already been canceled, nothing happens.
get_aspect(pos)
Gets the aspect of the signal at pos. The aspect format is described in the Signal page.
Same warnings apply as for can_set_route.
Events
In a LuaAutomation ATC controller, an event has the following format:
event = { type = "<type>", <type> = true, -- additional content }
You can check for a specific event type by using
if event.type == "<wanted>" then -- ... do stuff end
or
if event.<wanted> == true then -- ... do stuff end
int
event = { type = "int", int = true, msg = <message>, message = <message>, -- For backwards compatibility only! }
Fired when an interrupt set by the interrupt function runs out. <message> is the message passed to the function.
For backwards compatibility reasons, the message is also contained in the event.message field.
ext_int
event = { type = "ext_int", ext_int = true, message = <message>, }
Fired when a node called interrupt_pos on this node's position. <message> is the message passed to the function.
digiline
event = { type = "digiline", digiline = true, channel = <channel>, msg = <message>, }
Fired when the rail receives a Digiline message.
Specific to the ATC rail
Functions
atc_send(cmd)
Sends the specified ATC command to the train and returns true. If there is no train, returns false and does nothing.
atc_reset(cmd)
Resets the train's current ATC command and returns true. If there is no train, returns false and does nothing.
cmd is actually ignored by the current version of Advtrains.
atc_set_text_outside(text)
Sets the text shown on the outside of the train and returns true. If there is no train, returns false and does nothing.
atc_set_text_inside(text)
Sets the text shown inside the train and returns true. If there is no train, returns false and does nothing.
get_line()
Returns the line property of the train, as a string. This string can be used to distinguish trains of different lines and route them properly.
This property is also used by the interlocking system for Automatic Routesetting.
If there is no train, the Lua program stored in the rail will exit immediately:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …/mods/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/atc_rail.lua:93: attempt to index upvalue 'train' (a nil value)
set_line(line)
Sets the line property of the train, as a string. On subway trains bundled with Advtrains, the line is automatically displayed on the outside of the trains, if it is a number between 0 and 9 (where 0 is displayed as “Line 10”).
This property is also used by the interlocking system for Automatic Routesetting.
If there is no train, the Lua program stored in the rail will exit immediately:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …/mods/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/atc_rail.lua:88: attempt to index upvalue 'train' (a nil value)
get_rc()
Returns the routing code of the train, as a string. This property is used by the interlocking system for Automatic Routesetting.
If there is no train, the Lua program stored in the rail will exit immediately:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …/mods/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/atc_rail.lua:104: attempt to index upvalue 'train' (a nil value)
set_rc(rc)
Sets the routing code of the train, as a string. This property is used by the interlocking system for Automatic Routesetting.
If there is no train, the Lua program stored in the rail will exit immediately:
2019-01-01 15:00:00: WARNING[Server]: [advtrains]LuaAutomation ATC interface rail at (0,0,0) : LUA Error: …/mods/advtrains/advtrains_luaautomation/atc_rail.lua:99: attempt to index upvalue 'train' (a nil value)
set_shunt()
Enables shunting mode for the currently passing train and returns true. This mode permanently restricts the train speed to 6 m/s (or 21.6 km/h).
If there is no train, returns false and does nothing.
atc_set_ars_disable(value)
Enables (value == false) or disables (value == true) interlocking for this train. The train will not trigger automatic route setting on signals based on ARS.
This function has essentially the same effect as the ATC command A<enable_interlocking>.
This function is available only in the luaatc-extensions branch of Advtrains.
atc_set_lzb_tsr(speed)
Adds a Temporary Speed Restriction at the current rail, so that the train is passing the rail at the specified speed, or at a lower speed.
This function has essentially the same effect as a Point Speed Restriction Rail.
- This function is available only in the
luaatc-extensionsbranch of Advtrains. - This function is available only when the approach callback mechanism is enabled.
Fields
atc_id
The ID of the train passing the rail. nil if no there is no train.
atc_speed
The current speed of the train passing the rail, in metres per second. nil if no there is no train.
atc_arrow
Whether the train is driving in direction of the arrows on the ATC rail. nil if no there is no train.
Note: this code does not indicate whether there is a train on the rail, as both false and nil evaluate to false:
-- BAD if atc_arrow then -- ...do stuff end -- GOOD if not atc_arrow then return end -- ...do stuff
Events
The LuaATC rail currently supports the following events:
train
event = { type = "train", train = true, id = <train_id>, }
Fired when a train enters the rail. The field id is the unique ID of the train, which is a 6-digit random numerical string.
If the world contains trains from an older Advtrains version, the string may be longer and contain a dot (.).
approach
event = { type = "approach", approach = true, id = <train_id>, }
Fired when a train approaches the rail. This event may be generated multiple times for the same train.
- This function is available only in the
luaatc-extensionsbranch of Advtrains. - This function is available only when the approach callback mechanism is enabled.
Approach callback mechanism
The approach callback mechanism is a new feature that allows LuaAutomation ATC rails to hook into the approach callback system, which is used by the Point Speed Restriction Rails (from advtrains_interlocking) or by Station/Stop Rails (by advtrains_line_automation). Since it is relatively a recent feature, it needs to be explicitly enabled.
At the time of writing (2019-12-18), this feature is available only in luaatc-extensions branch of Advtrains. To use this branch, clone the Git repo in the Minetest mods directory and then git checkout luaatc-extensions on the mod directory.
To enable the feature, define the following global variable in the local environment of the ATC rail:
-- To enable approach callback only in arrow direction __approach_callback_mode = 1 -- To enable approach callback in both directions __approach_callback_mode = 2
The event approach will then be generated when a train approaches (which could happen anytime).
You'll have to consider the following when setting up approach callbacks:
- Approach callbacks might be generated multiple trains for a same train. If you call
atc_set_lzb_tsr, you'll have to call it on every run of the approach callback. - A reference to the train will be available while executing this event, so functions such as
atc_sendandatc_set_text_outsidemay be used. On subsequent interrupts however, this reference will no longer be available until the train enters the track. - The approach callbacks are executed synchronously during the train step. This may cause unexpected side effects when performing certain actions (such as switching turnouts, setting signals/routes) from inside such a callback. It is strongly encouraged to only run things that are absolutely necessary at this point in time, and defer anything else to an
interrupt(). Here are things that are safe to run from an approach callback:- Accessing and setting global environment
Trivia
The LuaAutomation ATC rail has the same texture as the ATC controller rail, but its functions are different.

